Reclaiming Storage by Cleaning Up DFS Cache and Conflict/Deleted Files
Recently, I encountered a disk space issue on a file server where the System Volume Information folder was occupying a significant amount of space due to DFS (Distributed File System) caching. During the initial migration to the new file server, a large cache size had been set for DFS. However, now that the files are more static, such a large cache is no longer necessary, but DFS continues to reserve this space.
To help others reclaim this lost storage, here’s a streamlined guide on how to clean up DFS cache, specifically targeting the ConflictAndDeleted folder, which can accumulate excessive data.
Steps to Clean Up the ConflictAndDeleted Folder
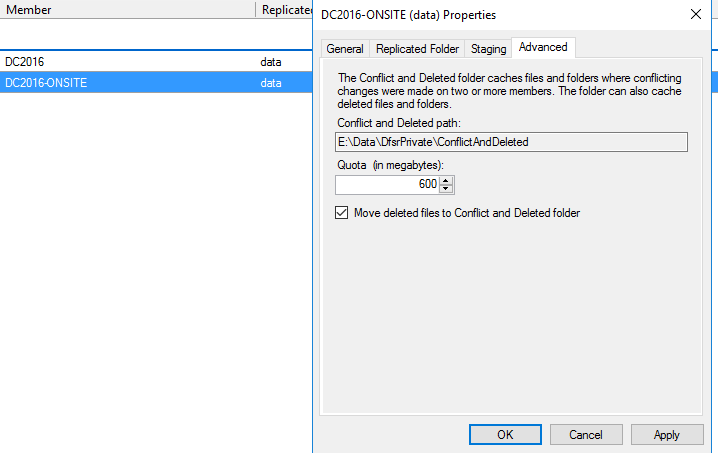
In my case, I needed to lower the Conflict and Deleted Quota first. Here is a screenshot within the DFS Management Interface. Right-click the member, select properties, and go to the Advanced Tab:
Using WMI for a Quick Cleanup
Instead of going through the more disruptive process of lowering the quota and restarting the DFS services, you can clean up the ConflictAndDeleted folder quickly using WMI. Here’s how:
Open Command Prompt as Administrator
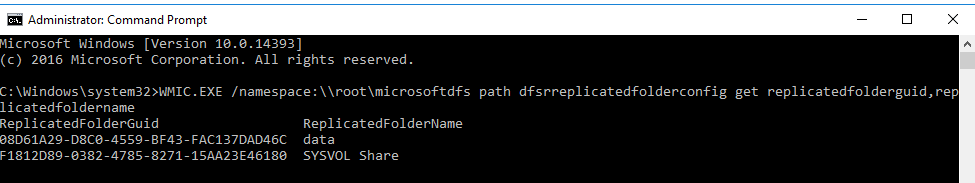
On your DFSR server, open a Command Prompt with administrator privileges.Obtain the Replicated Folder GUID
Run the following command to get the GUID of the replicated folder:
1
WMIC.EXE /namespace:\\root\microsoftdfs path dfsrreplicatedfolderconfig get replicatedfolderguid,replicatedfoldername
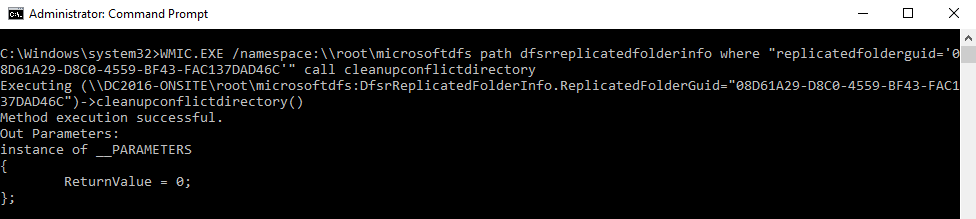
Clean the ConflictAndDeleted Folder Now, run the following command, replacing
1
WMIC.EXE /namespace:\\root\microsoftdfs path dfsrreplicatedfolderinfo where "replicatedfolderguid='<RF GUID>'" call cleanupconflictdirectory
This process will empty the ConflictAndDeleted folder, and the ConflictAndDeletedManifest.xml file will be removed, freeing up disk space.
Example:
1
WMIC.EXE /namespace:\\root\microsoftdfs path dfsrreplicatedfolderinfo where "replicatedfolderguid='08D61A29-D8C0-4559-BF43-FAC137DAD46C'" call cleanupconflictdirectory
By following these methods, you can effectively reclaim the storage being consumed by outdated DFS cache and deleted files. If your file server is static, this can be a significant space saver.